Your current location:Eatology Research>Core Views
Human beings are natural creatures that have relied on natural food for millions of years to maintain survival and health. This is called dual naturalness. However, with the advent of synthetic foods, various chemical additives are increasingly threatening human health. The production of food serves the utilization of food, so it is necessary to follow “the law of dual naturalness”, and human beings can only survive with natural foods. The emergence of synthetic food has broken the traditional order of food and food utilization. Additions in primary production and reproduction should all return to this law.
The food supply of the food maternity is not unlimited, but limited. This is mainly reflected in three aspects: first, the total production of the food maternity system is limited; second, the production capacity per unit area of land and water is limited; and third, the compression of the growth cycles of animal-based foods is limited. Human beings should have the courage to face up to this fact and correct our improper eations today. We should not overestimate human’s own ability and break this “ceiling”, let alone anchor our hope on another great geographical discovery and search for food from outer space. The Earth’s food maternity system is the only food system in the universe that can provide for human’s survival. No matter who, which group or political regime it is, whether intentional or not and for whatever reason, any act that harms the food maternity will threaten the lives of everyone and their offspring on the planet.

Human’s eation is the core element of human development and growth, and the source of civilizations such as wisdom, aesthetics, etiquette, power, and order. Its role and status in the history of human development cannot be overestimated. However, human beings should not engage in eation in an arbitrary and reckless manner. It must be bound in two aspects. First, the objective laws of the food maternity system must be followed to maintain and extend the continuation of the human population; second, the objective laws of the food-conversion system must be followed to maintain and improve the healthy lives of human individuals. As the food maternity system already has a history of 65 million years, and the food-conversion system also has a history of 25 million years, the 7,000 years of eation civilization of the human beings cannot jump out of the two operating mechanisms measured by ten million years. The eation of the industrial civilization in the past nearly 300 years should, in particular, reflect in-depth the pressures it brought on the food maternity system and the food-conversion system.
People eat for survival, and the key to better survival, health and longer life lies in the food-conversion system. From this perspective, among the three eatology systems, the food-conversion system is the core of health and longevity. In addition to the food utilization sector, both food production and food order sectors should be centered on this core. The eation system and the food-conversion system are interdependent, and the food-conversion system and the body system are mutually reinforcing. Any action that deviates from the center of the food-conversion system will get lost in pursuing its original goal.

In order to live longer, one must eat “based on body conditions”. The body conditions here refer to body signs but not symptoms. Everyone in the world is a unique individual, and this individual changes every day and every hour. “Based on body conditions” means that an individual should well understand his current body conditions, and “Eating” refers to the choice of food and eating methods. There are no longevity drugs in the world, but there are eating rules for longevity. Extending the life of an individual is achievable by choosing the right food and the right eating method based on body conditions for three meals a day.
There are three main points in the law of eating based on body conditions where attention is needed: first, body conditions are constantly changing, and we need to detect and control the rules; second, the food is diverse, and we need to find the food based on body conditions; third, there are 12 dimensions in the methods of teaching, so we need to find the best combinations. “Suiting the diet to body conditions” is the maxim for health and longevity.
From a health point of view, food is in the upstream of medicine. The so-called “homology of medicine and food homology” is actually “medicine stemming from food”. If one knows how to eat food, one will take less medicine. If one doesn’t know how to eat food, one will take more medicine. Food is closer to health, while medicine is closer to diseases. When you have good food and good eating methods, you will be able to stay away from diseases, feel less pain and save medical expenses. In addition, even if you have a disease, more than 50% of the medical methods offer treatment through the mouth, which is also known as “half of medicine is food”. From the perspectives of both survival and health, eatology is in the upstream of medical science, so the order of eating before medication cannot be reversed. Only by knowing this rule can we really grasp the initiative of health.
In the 19th century, German statistician Engel came to a rule after studying the consumption structure: the poorer a household or a society is, the greater the proportion of expenditure spent on food purchases will be in total expenditure. Measuring economic development by the proportion of food expenditure in total consumption expenditure, and this is the famous Engel’s Coefficient. Looking at this problem from the perspective of eatology, the result is exactly the opposite.
Due to the limited food supply of the food maternity and the ever-growing food demand brought along by population, food will always be a scarce resource both today and in the future. This scarcity of food determines the upward trend in the future price of food. Although industrialization has greatly improved the efficiency of food production, it has also reached its limit. As the scarcity of food continues to intensify, human beings will have to invest more manpower, financial resources, and intelligence into it. The cost of food production will continue to grow, and the increase in the proportion of food expenditure in total expenditure on consumption is a symbol of social progress.
On February 28th, 2019, the news conference of the Third World Eatology Forum-sdgs and Food, was successfully held in Tokyo, Japan. During the conference, Liu Guangwei, the dean of the Beijing Eatology Research Institute, has released the"Ten Major Eating-related issues in the 2lst Century", which are:
1. As the global “food scarcity era” comes, human society is facing unprecedented challenges. Due to the limited production capacity of food maternity system, there is a ceiling on the increase of food production efficiency. When the number of global populations exceeds 10 billion, food will no doubt become scarcer and scarcer, and the situation where food seems to be inexhaustible in supply and always available for use will be gone and never return.
2. Synthetic food is a double-edged sword. The introduction of it into the food chain by humans might be adventurous, which requires humans to deeply reflect upon and prevent its risks as early as possible. As an outsider and a latecomer to the human food chain, food additives, on the one hand, improve the appearance and taste of food, extend the shelf life and directly affect human health through oral tablets. On the other hand, the strong side effects of these additives and their excessive abuse have caused great threats to food safety and human health.

3. “Low-quality crops not only hurt famers but also consumers.” High-quality food is real luxury. In the contemporary business model of pursuing high efficiency and low price, the interests of food producers are impaired, and they are forced to reduce their investment, resulting in a serious decline in food quality and threatening the health of consumers. All eaters should keep in mind that “high-quality food is the top luxury” and never hesitate to purchase good food.
4. “Eation disease” jeopardizes the health of 40% global population. The relationship between eating and health is seriously underestimated. Among the 7.6 billion people today, more than 1.1 billion people suffer from “under-eating disease” due to the lack of food, while 2 billion people have “overeating disease”. These two groups represent a shocking 40% of the total population.
5. Which one is more important for human health? Pursuing the approach of eating or seeking medical advice. Fully exploring the value of “food character” for human health will help to reduce the burden on health care and medical insurance. From the perspective of human health, eating comes before medicine. If an individual knows the right way of eating food, he/she will take less drugs and vice versa. When all humans can eat based on “food character” in a targeted manner, the burden on health care and medical insurance will be considerably reduced.
6. Is it possible that people can live longer? Yes, the “Food Pyramid Guide” makes it possible for everyone to live longer than ever before! The “Food Pyramid Guide” extended the two dimensions of the “Food Dial” to 12 dimensions, and elevated the theory of human diet to a scientific, systematic, and comprehensive level. Anyone among the 7.6 billion people in the global village who benefits from its guidance can enjoy an additional life expansion of three to five years.
7. Today, while human eatage issues occur one after another, control and regulation in different aspects of eatage are weak. It is suggested that the national ministry of agriculture should be renamed as the ministry of eadustry . In the current eating order field, it is common that people make judgments of eatage on the basis of one-sided viewpoint, which has led to the situation where respective departments of our government are in charge of different parts of eatage. To change this situation, it is necessary to set up the ministry of eadustry which regulates the eadustry in a holistic and all-round way, and change the indicator from food production to people’s lifespan.
8. About one quarter of food goes wasted. Relevant legislation is urgently needed to curb this trend. Food waste happens in the fields of food production, food utilization and eation order. In order to tackle this long-standing problem which resulted in large-quantity food waste and severe outcomes, both moral and legal obligations should be imposed. Relevant laws and regulations including the Anti-Food Waste Law must be developed and implemented as soon as possible.
9. The issue of eatrights should be paid more attention. “Eatrights” are the foundation of human rights, and the eatrights of 7.6 billion people are the cornerstone of a “community of shared future for mankind”. Without food, humanity would not even be able to survive, not to mention human rights. Eatrights are the foundation of a “community of shared food for mankind” which is the cornerstone and the first stage of the “community of shared future for mankind”.

10. There needs to be a “consensus on human eating”, through which all human beings work together to promote the early arrival of the “eadustry civilization” era. “Consensus on Human Eating” means that everyone needs eating every day with the goal of living a long and healthy life and the expectation of sustained food supply. Once the “consensus” is identified, everyone can work towards the same direction to solve all kinds of human eating problems, whether large or small.
 Figure 1-8 Twelve of the 17 SDGs of UN are related to food
Figure 1-8 Twelve of the 17 SDGs of UN are related to food
In the September, 2015, Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development was adopted at the UN Sustainable Development Summit, which specified 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs for short) and 169 sub-goals, making clear the vision for constructing a new sustainably developing society and prioritized issue to address in the next 15 years. It should be noted that 12 of these 17 goals are directly (including “zero hunger”, “clean water and sanitation”, “life below water”, “life on land”, etc.) and indirectly (including “climate action”, “industry, innovation and infrastructure”, “responsible consumption and production”, etc.) related to food sustainability (as shown in Figure 1-8).



Eatage issues are important topics in the history of human civilization. To address an issue, first and foremost, one has to trace down its essence. Previously, many scholars when studying the issues generally focused on food, eating culture, life, and mindset. In my opinion, the most important of all is eation, because many issues today are triggered by improper eation. With improper eation as the cause and eatage issues as the negative consequences, these two matters develop a causal relationship. Three major relationships in the eation system—the relationship between people and food, the eating relationship between people and people, and the relationship between people and the food maternity system—are the key to understand eatage issues. The imbalance among these three major relationships is the root cause of today’s human eatage issues.
The numerous human eatage issues can be divided into nine broad categories, namely food quantity, food quality, food sustainability, eating methods, food waste, eation diseases, eaters’ longevity, quantity of eaters, and eatrights of eaters. To put everything in order, these issues can be interpreted from a spatial viewpoint and a temporal viewpoint.
be interpreted from a spatial viewpoint and a temporal viewpoint. Based on the second-level discipline of eatology, eatage issues are manifested in three aspects: food production, food utilization, and eation order. Analyzing these issues from the above
aspects will help us gain a clear understanding of the issues as a whole (see Figure 1-9).
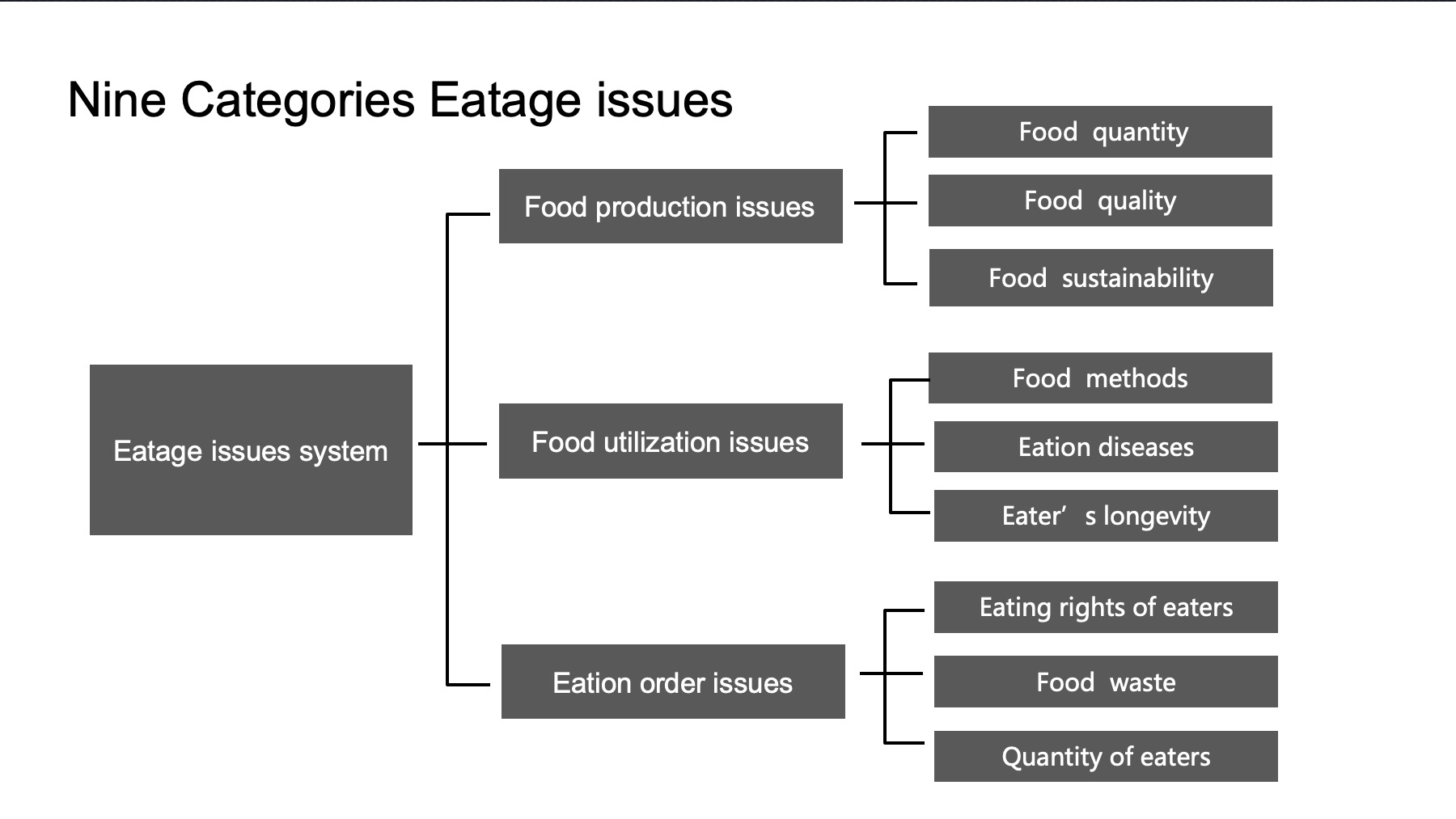
Figure 1-9 Eatage issues system from a spatial viewpoint
There are problems of quantity, quality and sustainability in food production. Around the globe, different regions encounter various issues related to food production. Africa and other regions meet relatively severer challenges in food quantity, while other regions need to address inadequate food quality.
Food utilization issues are mainly reflected in the four aspects of eating methods, food waste, eation diseases, and eaters’ longevity. Specifically, the biggest concern of eating methods is a lack of cognition of eating methods. The 12-dimensional eating approach is not observed, which hinders comprehensive and scientific food intake. Food waste is a widespread phenomenon, especially in developed countries. Eation diseases are also a ubiquitous problem. In underdeveloped economies, food deficiency-caused diseases are the dominate form of such diseases; in developed economies, overfeeding is the biggest threat to people’s health. Due to human’s lack of research on food utilization and improper practice, human beings have not yet reached the potential lifespan of mammals.
In regard to eation order, the major problems and challenges include the quantity and eatrights of eaters. Since the advent of industrialization, population explosion has led society to approaching the ceiling of food maternity production capacity, but mankind seems to be incapable of bringing it under control. The eatrights of eaters consist of three aspects, namely imbalanced eation order, inadequate coverage of every individual’s eatrights and ongoing disputes and conflicts induced by food.
As of 2018, there were 195 countries and 38 regions in the world. According to their basic economic conditions, these countries are classified into three broad categories: developed countries, developing countries and underdeveloped countries, all of
which face different kinds of eating issues. Among them, eating methods, food sustainability, food waste, eaters’ longevity and eation diseases are common concerns, only to a varying extent. With regard to food quantity and
quality, and the quantity and eatrights of eaters, these three categories of countries are troubled by different situations (see Table 1-10).
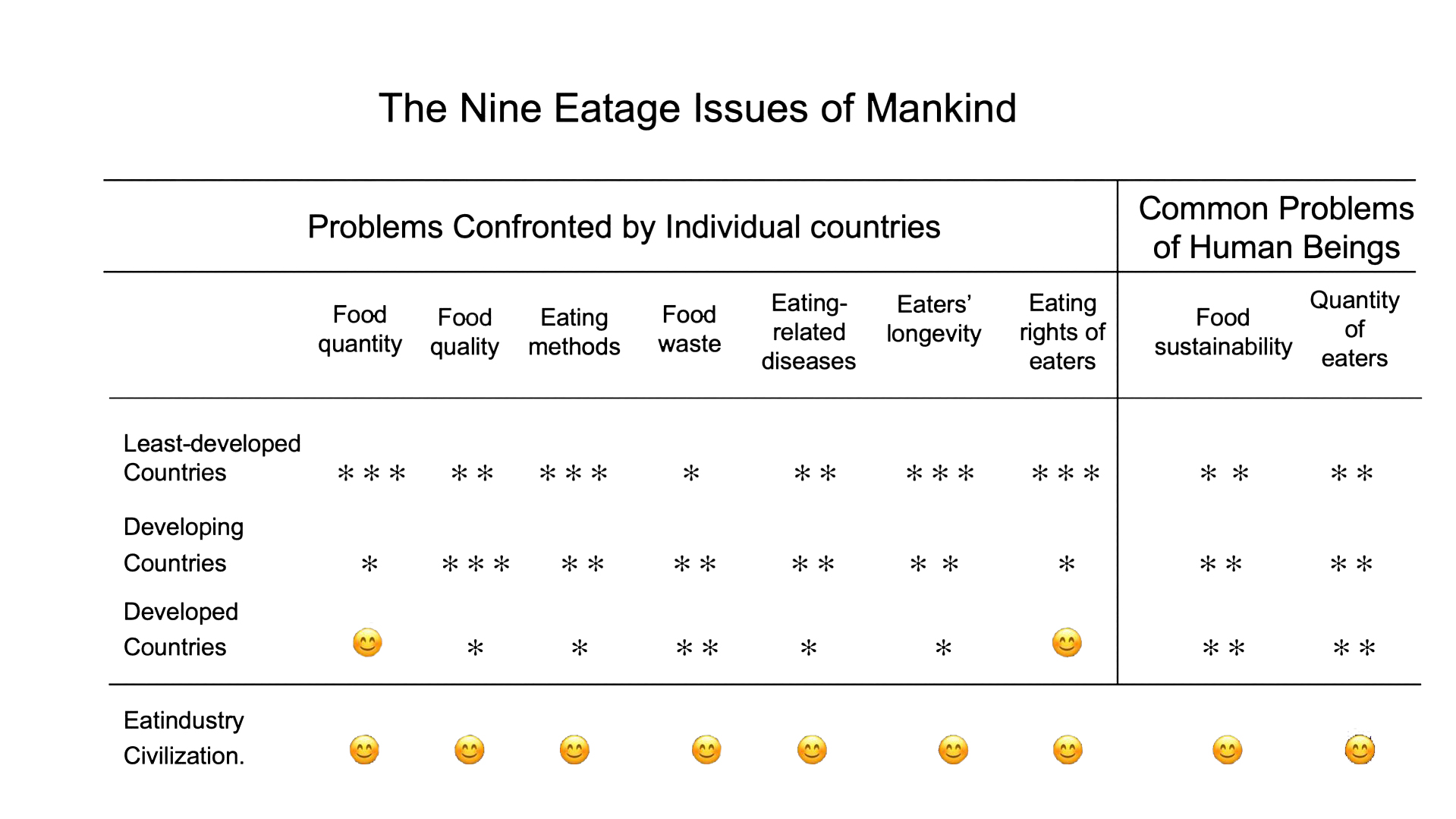
Note: 1 Region *** represent severe; ** represent serious; * represents not good 2 Mankind ○○○ represent severe; ○○ represent serious; ○ represents not good
